Is Galvanized Steel Safe for Raised Garden Beds?
Raised garden beds offer numerous advantages, including better soil control, improved drainage, and easier access for gardeners. When choosing a material for constructing these beds, galvanized steel often emerges as a contender due to its durability and affordability. However, concerns regarding the safety of using galvanized steel around edible plants persist. This article examines the potential risks and benefits of using galvanized steel for raised garden beds, providing information to help gardeners make informed decisions.
What is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is steel coated with a layer of zinc. This zinc coating protects the steel from rust and corrosion, significantly extending its lifespan. The galvanization process can involve either hot-dipping or electrogalvanizing. Hot-dipping involves submerging the steel in molten zinc, while electrogalvanizing uses an electrical current to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto the steel's surface.
Potential Risks of Using Galvanized Steel
The primary concern with using galvanized steel in raised garden beds revolves around the potential leaching of zinc into the soil. Zinc is an essential micronutrient for plants, but excessive amounts can be toxic. In highly acidic soils (pH below 6.0), the zinc coating can react, increasing the likelihood of zinc leaching into the soil. This leaching can potentially contaminate the soil and be absorbed by the plants grown within the raised bed.
Older galvanized steel, particularly that galvanized before the mid-1980s, may contain lead. While modern galvanizing processes have largely eliminated lead, older steel structures might pose a lead contamination risk. Lead is a heavy metal that is harmful to humans, especially children, and should be avoided in food production environments.
Benefits of Using Galvanized Steel
Despite the potential risks, galvanized steel offers several advantages as a material for raised garden beds. Its durability is a significant benefit. The zinc coating protects the steel from rust and corrosion, leading to a long lifespan, unlike untreated wood which can rot and decompose over time. This durability translates to a lower long-term cost compared to other materials that require more frequent replacement.
Galvanized steel is also relatively inexpensive compared to other durable options like stainless steel or composite lumber. It is readily available at most hardware stores and can be easily cut and assembled into various shapes and sizes to suit individual garden needs. Its strength and rigidity also make it suitable for taller raised beds that might not be feasible with other materials.
Mitigating the Risks
Several strategies can mitigate the risks associated with using galvanized steel for raised garden beds. One of the most effective methods is to create a barrier between the steel and the soil. Lining the inside of the galvanized steel bed with a heavy-duty plastic liner or landscape fabric effectively prevents direct contact between the soil and the zinc coating, minimizing the potential for zinc leaching.
Regularly monitoring the soil pH is also crucial. Maintaining a soil pH above 6.0 reduces the risk of zinc leaching. Adding amendments like lime can help raise the pH if necessary. Conducting soil tests periodically will help ensure optimal pH levels and monitor nutrient content.
Alternatives to Galvanized Steel
Gardeners concerned about using galvanized steel can consider alternative materials. Untreated wood, such as cedar or redwood, is a popular choice due to its natural resistance to rot and insects. However, it has a shorter lifespan compared to galvanized steel. Composite lumber, made from recycled plastic and wood fibers, offers durability and longevity but is a more expensive option.
Stainless steel is another durable and long-lasting alternative, but it comes with a higher price tag. For those seeking a more natural approach, stone or concrete blocks can be used to create raised beds, though these options can be more labor-intensive to install.
Choosing the Right Material
The decision of whether or not to use galvanized steel for raised garden beds depends on individual circumstances and risk tolerance. Weighing the potential risks of zinc leaching against the benefits of durability and cost-effectiveness is essential. By understanding the potential concerns and employing mitigation strategies, gardeners can make informed decisions about choosing the best material for their raised garden beds.
Understanding the properties of galvanized steel, the potential risks associated with its use, and the available mitigation strategies empowers gardeners to make informed choices and cultivate thriving gardens.
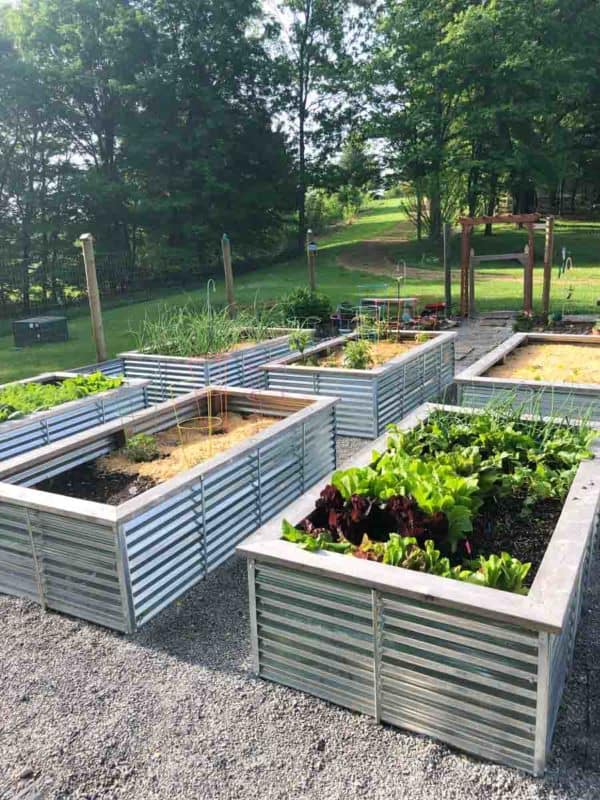

Galvanized Steel Raised Garden Beds Plans Tutorial Growfully

Galvanized Raised Beds Big And Small Kits Diy Options

Raised Garden Beds Galvanized Metal Vs Wood Huw Richards

Raised Garden Bed Materials What S Good Epic Gardening

Are Galvanized Steel Garden Beds Safe Epic Gardening

5 Misconceptions Of Metal Garden Beds Why They Are Safe Sunnydaze Decor

Galvanized Raised Beds Big And Small Kits Diy Options

Are Galvanized Steel Garden Beds Safe Epic Gardening

Is It Safe To Use Galvanized Metal For Raised Beds Crate And Basket

How To Grow Vegetables In A Galvanized Raised Garden Bed Gate
Related Posts